Oriental Rugs Dictionary
Unicorn Tapestries
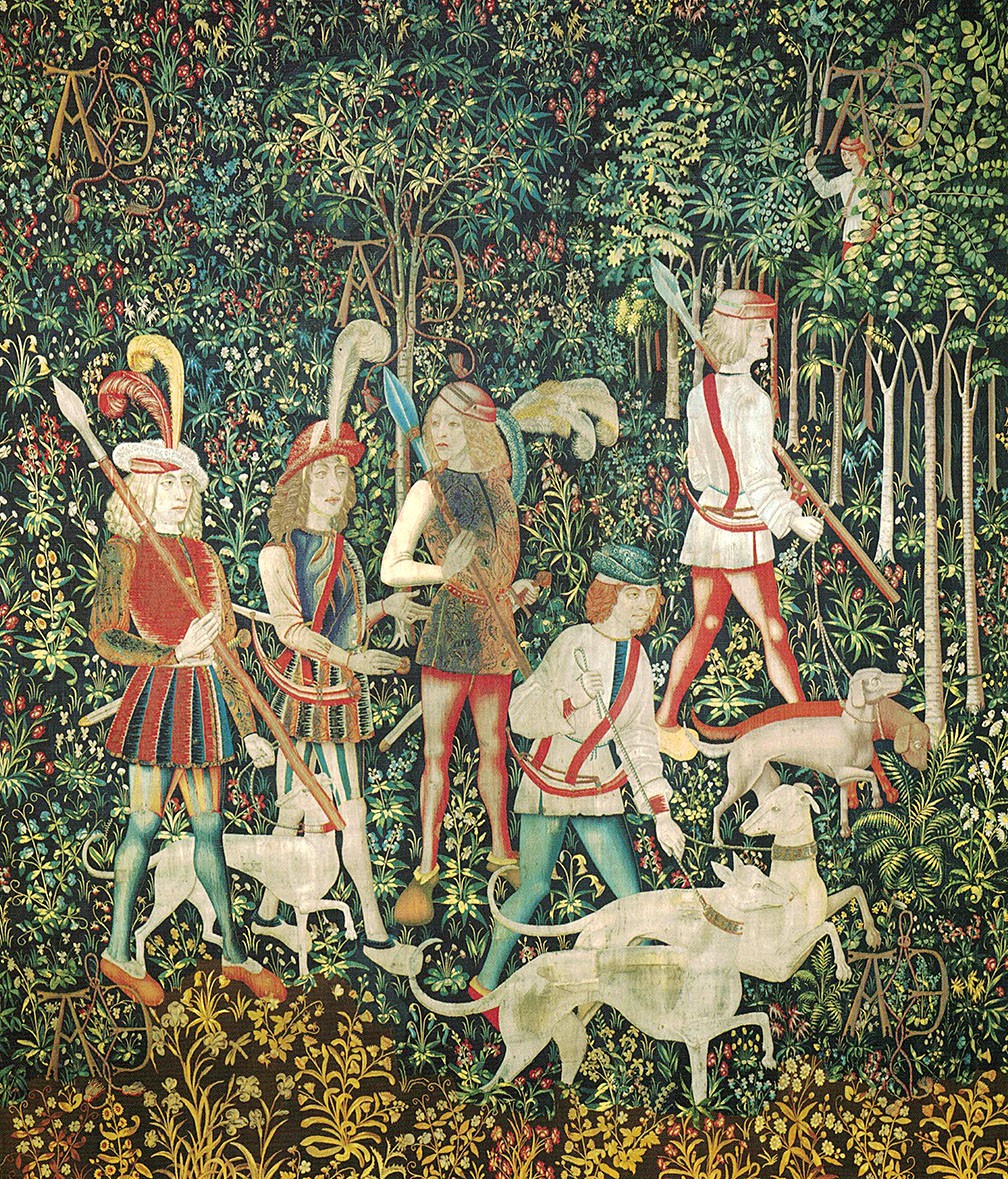
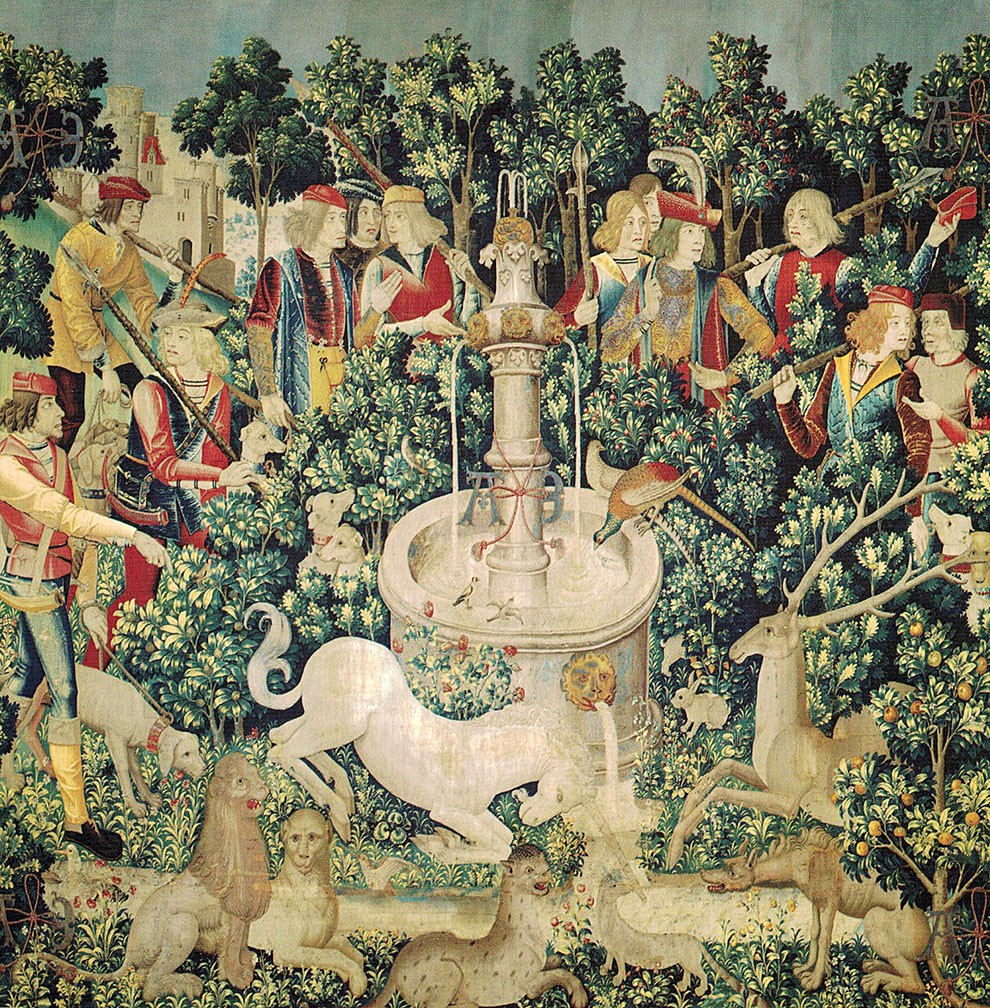
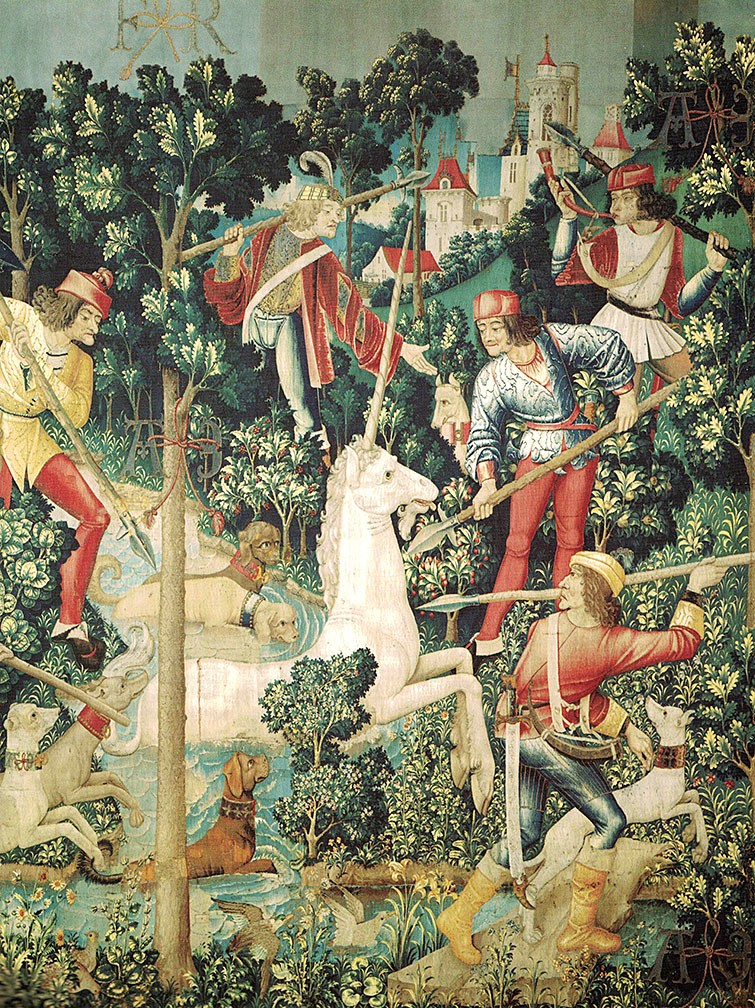
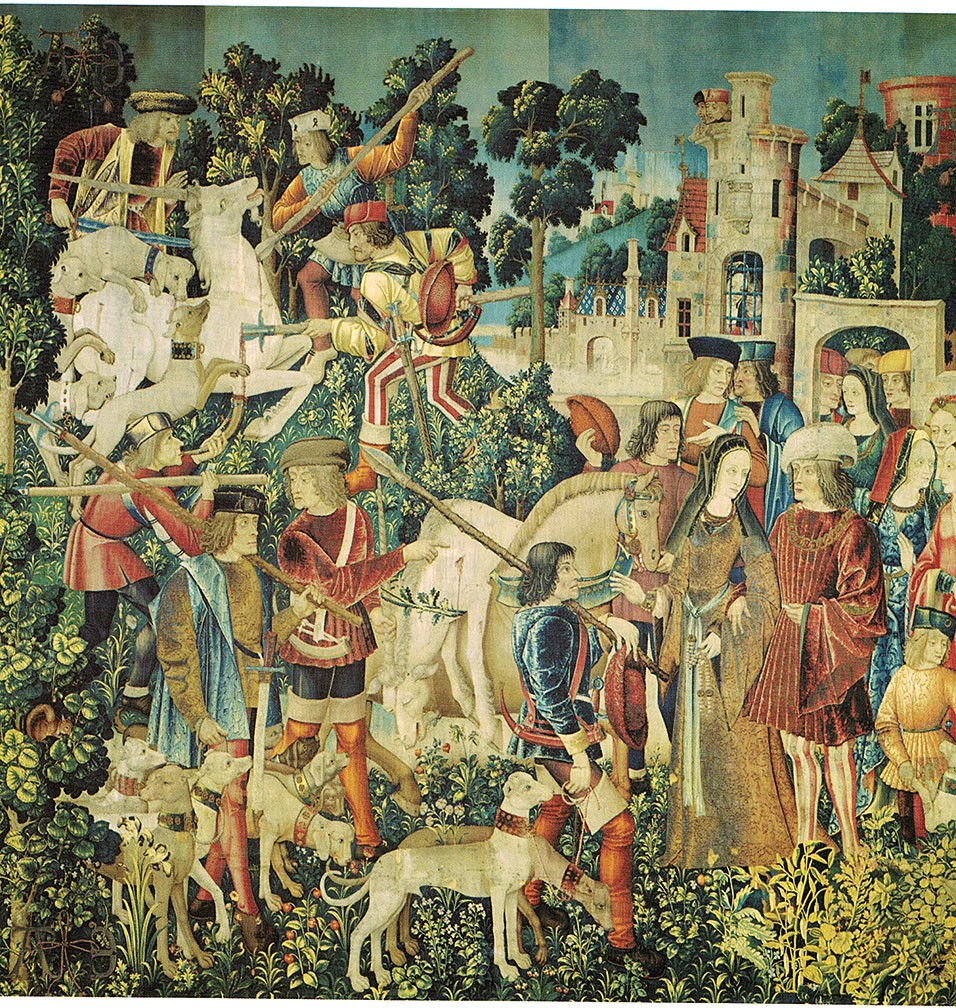
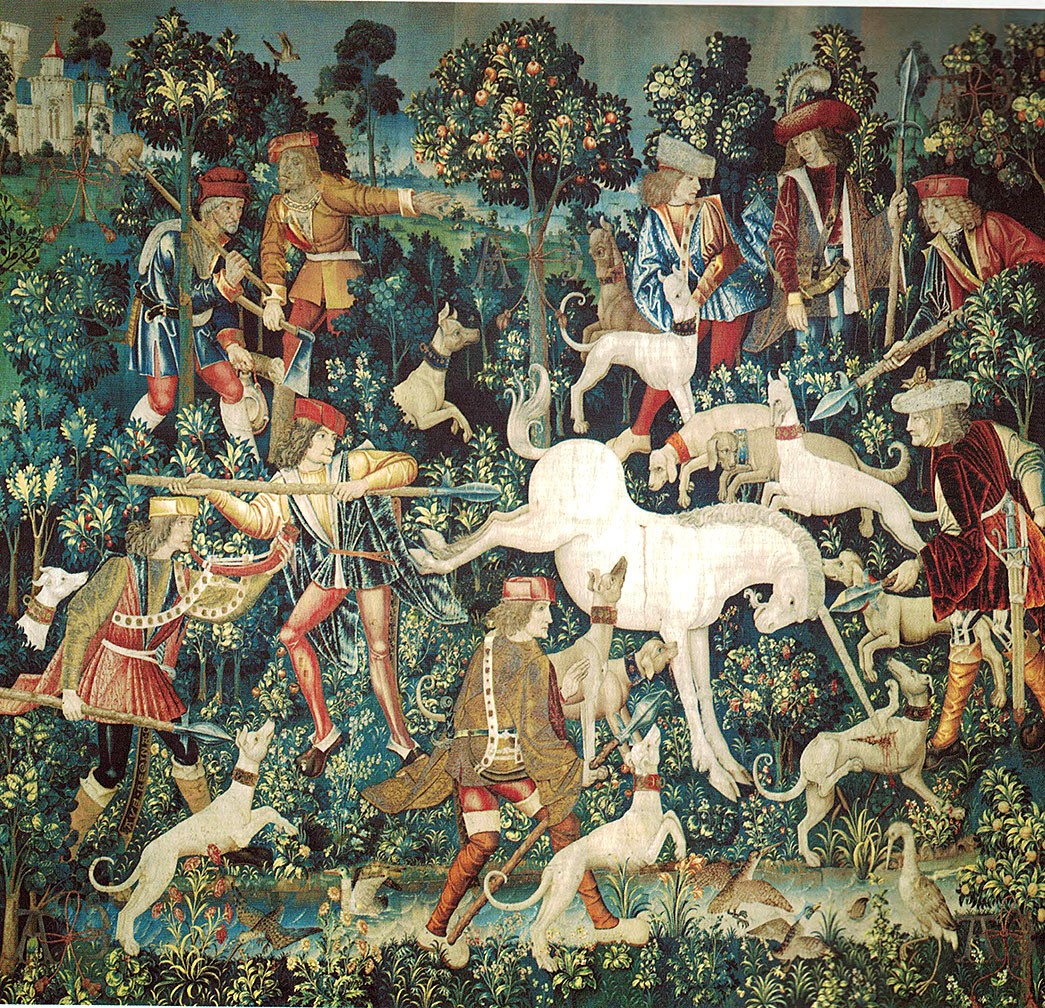
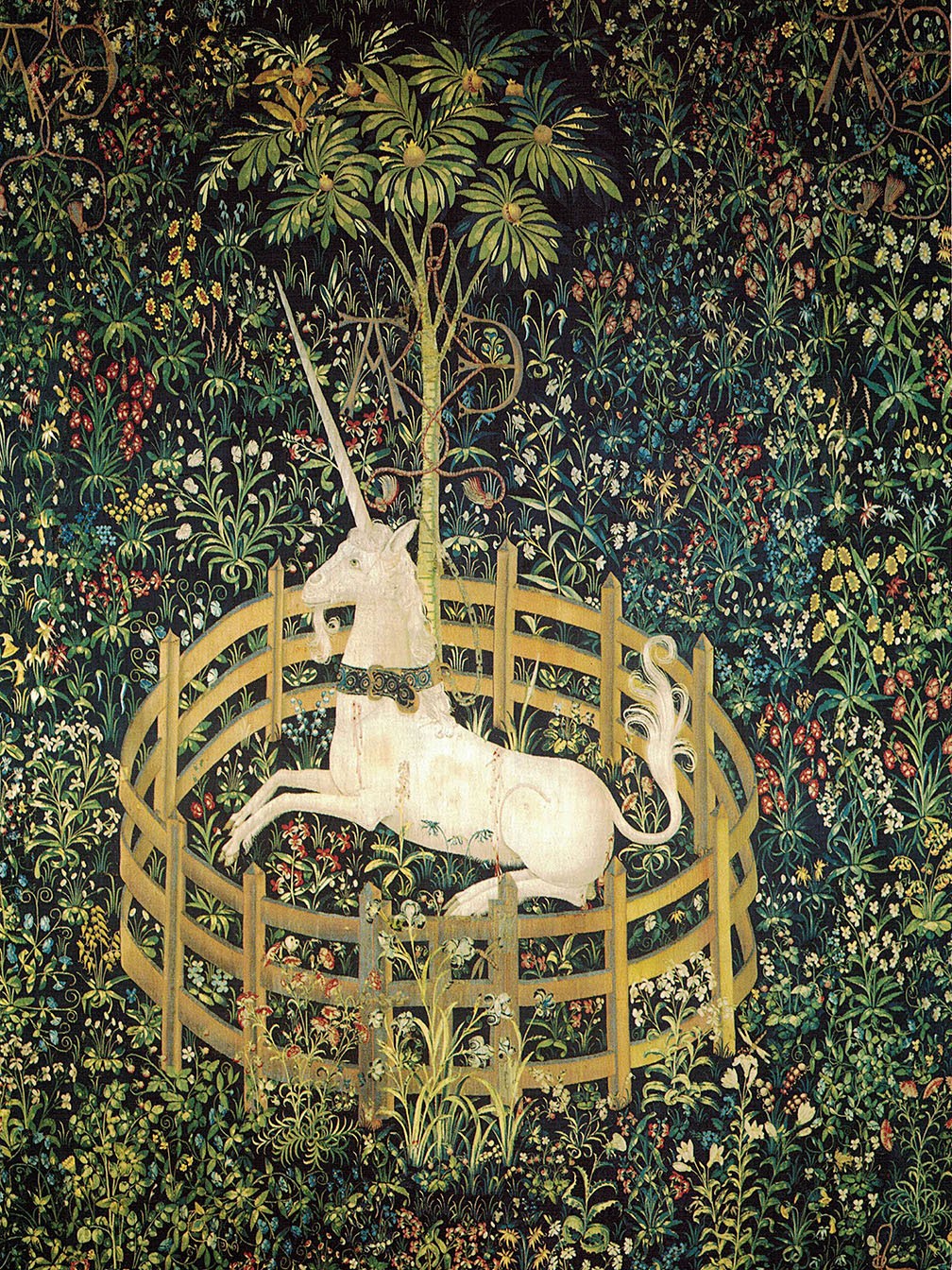
The Hunt of the Unicorn or the Unicorn Tapestries (French: La Chasse à la licorne) is a series of European tapestries dating from the late Middle Ages. This series of seven tapestries now in The Cloisters in New York was possibly made – or at least designed – in Paris at the turn of the sixteenth century. They are one of the canonical works of Late Middle Ages/Early Renaissance art and show a group of noblemen and hunters in pursuit of a unicorn through an idealised French landscape. The tapestries were woven in wool, metallic threads, and silk. The vibrant colours, still evident today, were produced from dye plants: weld (yellow), madder (red), and woad (blue). First recorded in 1680 in the Paris home of the Rochefoucauld family, the tapestries were looted at the French Revolution. Rediscovered in a barn in the 1850s, they were hung at the family's Château de Verteuil. Since then they have been the subject of intense scholarly debate about the meaning of their iconography, the identity of the artists who designed them, and the sequence in which they were meant to be hung. Although various theories have been put forward, as yet nothing is known of their early history or provenance, and their dramatic but conflicting narratives have inspired multiple readings, from chivalric to Christological. Variations in size, style, and composition suggest they come from more than one set, linked by their subject matter, provenance, and the mysterious AE monogram which appears in each. One of the panels, "The Mystic Capture of the Unicorn", survives as just two fragments. James J. Rorimer speculated in 1942 that the tapestries were commissioned by Anne of Brittany, to celebrate her marriage to Louis XII, King of France in 1499. Rorimer interpreted the A and E monogram that appears in each tapestry as the first and the last letters of Anne's name. Margaret B. Freeman, however, rejected this interpretation in her 1976 monograph, a conclusion repeated by Adolph S. Cavallo in his 1998 work. Tom Campbell, former Director of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, recently acknowledged that experts "still do not know for whom or where [the tapestries] were made." So far, scholarly efforts to explain the AE and other inscriptions, to identify the few heraldic symbols, and to coherently account for the puzzling narratives have met with limited success.